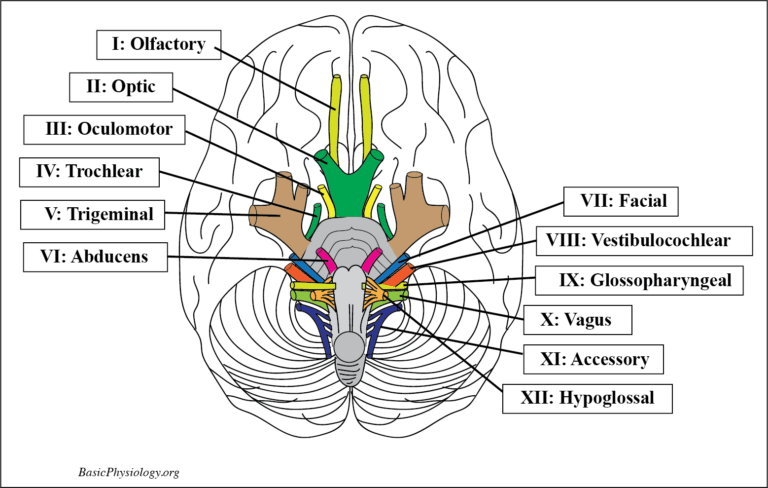
A. Cranial Nerves:
There are numerous connections between the (central) brain and the body but one of the most important ones are the cranial nerves.
As the name implies, these are nerves that come from the cranium (= skull), hence the name ‘cranial’.
There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves!
Pairs? Yes, every cranial nerve comes as a pair; left and right. So, in fact, we have a total of 24 cranial nerves.
| 5. These are the 12 cranial nerve pairs: | ||
| I –Olfactory nerve
II – Optic nerve III – Oculomotor nerve IV – Trochlear nerve |
V – Trigeminus nerve
VI – Abducens nerve VII – Facial nerve VIII – Vestibulocochlear nerve |
IX – Glossopharyngeal nerve X – Vagal nerve XI – Accessory nerve XII – Hypoglossal nerve |
Whew! That’s a lot! And, of course, we have to discuss them …
I drew a picture of all these nerves where they emerge from the bottom of the brain.
You don’t have to remember all these structures (unless you want to become a cranial nerve doctor!).
The idea is just to show you how all these nerves come out of the bottom of the brain.
I: Olfactory nerve:
This is a sensory nerve bundle that connects the sensory cells in your nose to the olfactory bulb in the brain.
II: Optic nerve:
This is a sensory nerve bundle that connects the light receptors in your eye (retina) to the visual cortex, located in the back of the brain.
III: Oculomotor nerve:
This is a motor nerve bundle, from the midbrain, to the eye (=oculo) that controls a) eye movements and b) pupil diameter
IV: Trochlear nerve:
This is also a motor nerve bundle, also from the midbrain, that controls the oblique movements (downward, out- and inward view) of the eye.
V: Trigeminal nerve:
As you can guess (=tri!); this cranial nerve consists of three separate bundles:
- Ophthalmic: sensory signals from the upper part of your face, around the eyes
- Maxillary: sensory signals from the middle part of your face, cheek and upper lip
- Mandibular: sensory signals from the lower part of your face, chin, lower lip and ears but also has a motor function of your jaw muscles and ear.
VI: Abducens nerve:
This is a motor nerve bundle that controls the outward movements of the eye (abduct= move away from the axis of the body).
VII: Facial nerve:
This nerve provides both sensory and motor functions such as:
- Contracting several muscles in the face and jaw
- Innervating glands such as the salivary glands and tears
- Innervating taste sensors in the tongue
- Sensory information from the skin of the ear
VIII: Vestibulocochlear nerve:
This nerve consists of two sensory parts:
- the cochlear part; sensory information about the sound from your ear
- the vestibular part; transmits information about your movements of your head
IX: Glossopharyngeal nerve:
This nerve consists of both sensory and motor functions:
- sensory information from the throat, from the sinuses in the skull and part of the tongue
- stimulating the stylopharyngeus muscles in your throat
X: Vagus nerve:
Contains also both sensory and motor nerves:
- sensory information from the ear canals
- sensory information from heart and intestines
- motor control of the throat muscles
- motor control of the intestines
- sensory information from the tongue
XI: Accessory nerve:
Motor nerve that controls the muscles in the neck
XII: Hypoglossal nerve:
Motor nerve that controls the movements of the tongue
Whowww! That’s a lot of nerves! Do we have to know all of them? NO.
Unless you want to become a cranial nerve specialist, most ‘medical persons’ only know/remember a few cranial nerves.
It depends very much on your speciality which nerves are really important, just like anything else in medical sciences.
For the basic physiologist, I have listed those nerves that are most prominent in our field.
These are (in my mind) the most important cranial nerves:
X: Vagus nerve
II: Optical nerve
I: Olfactory nerve
The vagus nerve (X) is so crucial to our body function that I have dedicated a special page for this nerve (coming ….).
The optical nerve (II) is also very important and quite complicated which necessitated another page! (H.4.1. Vision).
The olfactory nerve (I) is much simpler and easier but important too; therefore, another dedicated page (H.4.4. Taste and Smell)